If you’re a social media marketer, or your business engages in social media marketing, then last week’s beards-and-coronavirus misinformation fiasco should have been a huge wake-up call for you.
Here’s what happened.
Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you’re likely aware that a new coronavirus (COVID-19) has emerged, and it’s causing concern in pretty much all corners of the globe. Regardless of whether a country has experienced any cases on its own turf, everyone is glued to the media reports to stay abreast of the latest status, advice, and warnings.
On the morning of Wednesday February 26 2020, someone (original culprit unknown) posted an infographic that the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) created in 2017 for workers who are required to use facepiece respirators in their jobs. It was apparently (and very smartly) timed to align with “No Shave November,” to help those intending to grow beards in support of cancer awareness know what types of facial hair would prevent such respirators from working properly. The respirators aren’t effective if the hermetic seal isn’t intact on the skin, so this safety message was not only smart but necessary.

The problem is… on Feb 26, 2020, this infographic was erroneously shared as NEW information from the CDC as a warning to the general public about COVID-19. The dramatically incorrect message? Men with beards won’t be protected from the new coronavirus unless they shave to one of the styles that work with everyday facemasks.
But wait… it gets worse.
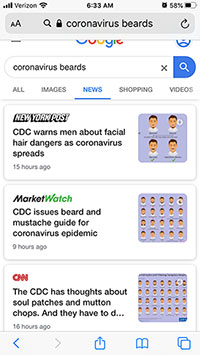
The media, never shy about jumping on new (and especially absurd) angles to fuel a 24/7 news story, seized that nugget WITHOUT FACT CHECKING, and transformed it into headlines such as:
- CDC Warns Men About Facial Hair Dangers as Coronavirus Spreads
- CDC: Shave Your Beards to Prevent Coronavirus
- These Beards May Make You More Likely to Catch Coronavirus
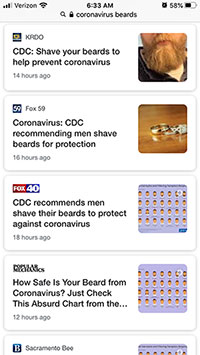
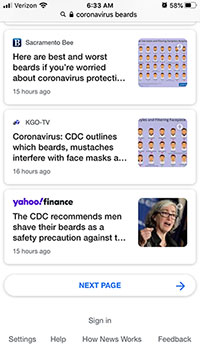
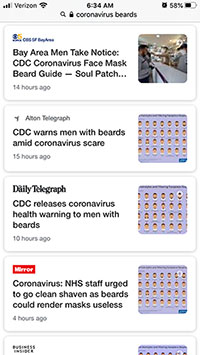
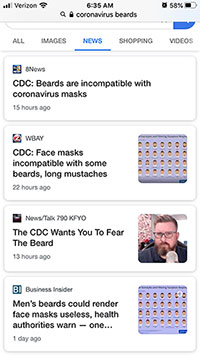
Within 24 hours, dozens of seemingly-credible news outlets shared this incorrect story as fact. Here’s what the first five pages of a mobile search for “coronavirus beards” returned on the morning of Feb 27:
Now, forget for a moment that we’re talking about epidemics, media alarmism, and the shyster-like use of “click bait headlines” as a marketing weapon.
The lesson for social media marketers is this: never EVER believe what you read – or worse, share it – unless you’ve checked the facts yourself. In this case, a quick Google search would have told you that dozens of outlets were reporting on it… but that meant diddly squat, because they were ALL wrong.
So, you can’t rely on “quantity of stories” to verify facts, which is tempting. Here’s what you CAN do:
- Check the original-named source. In this case, one hop onto the CDC website or their Twitter feed would have revealed that they made no such announcement. But ANYTIME you see a media report that claims that “so-and-so says”… go straight to so-and-so’s website and social channels to find out if it’s true.
- Check the media sources best known for reputable fact-checking. Two known for highest standards in accuracy and credible sourcing are Associated Press and Reuters. If they didn’t cover the story, it casts doubt on the veracity. (Note: Reuters didn’t cover the beard thing at all, and AP did just one story… on Feb 27 refuting the claim, with context and quotes sourced directly from the CDC.)
- Check the credibility of the media outlet you’re using. A helpful website, Media Bias/Fact Check, has a handy search tool that evaluates the bias and accuracy of media websites. While it’s by no means infallible or the only source available for such assessment, it’s certainly useful as an indicator. A quick search on this site reveals things like how often a media source uses loaded language to sway emotion vs. factual reporting, how deeply/accurately it checks its facts, and how often it skews facts/opinion to favor a political bias (either left or right).
You may be thinking “well, I’m a tourism destination/hotel company/attraction/restaurant, and I’m not likely to be sharing coronavirus stories, so this sort of fact-checking thing doesn’t really apply to me.”
Not so. Weird stuff, urban legends, outrageous claims and more are reported in the media all the time (broomstick challenge, anyone?)… and in your quest to keep your own social feeds interesting and relevant, you may pluck one out to spin with your own angle, and share it with the best of intentions.
So, the moral of the story is: check your facts and keep your beards on.
Bonus (related) tip: the tactic of using shock-and-scare to get attention isn’t just reserved for online. Learn about the time Alamo tried to casually scare me into upgrading to a “safer” car.
 get travel marketing tips
get travel marketing tips